Behavioral Targeting: What It Is and How to Do It in 2025
Behavioral targeting analyzes user behavior to deliver personalized marketing messages.
Examining online behaviors like search queries, purchase history, and content engagement is extremely important in marketing. It’s, in fact, the only way to create tailored experiences that resonate with individual users.
Numbers are on our side on this one.
Targeted advertising has been shown to secure an average of 2.7 times as much revenue per ad as non-targeted advertising.
Keep reading to learn how behavioral targeting can transform your marketing efforts and drive meaningful results. We’ll discuss different types of behavioral targeting, how to implement it, and whether it’s ethical or not.
“Advertising will get more and more targeted until it disappears because perfectly targeted advertising is just information.” - Dave Winer, American software developer.
P.S. Ready to take your behavioral targeting to the next level? Check out our list of the Best 31 Retargeting and Remarketing Agencies to find expert partners who can help refine your strategy and drive better results.
What Is Behavioral Targeting?
Behavioral targeting uses data on user actions—like purchase history and search queries—to deliver personalized marketing messages.
Key aspects include:
Data collection: Gathering first-party data from websites and mobile apps and third-party data from external sources.
Audience segmentation: Categorizing users into segments based on behaviors, such as purchase intent or content engagement.
Personalized content delivery: Creating marketing messages tailored to each segment's behaviors and interests.
In 2023, the global behavioral targeting market was valued at approximately $10.5 billion, with projections to reach around $29.8 billion by 2032. Do the math, and you’ll see a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.5% during the forecast period.
Basically, personalized marketing strategies are becoming more and more important in today's – and tomorrow’s – digital advertising campaigns.
What Is Behavioural Targeting vs Contextual Targeting?
Behavioral targeting uses first-party data and behavioral segmentation to predict purchase decisions, while contextual targeting delivers relevant content based on keywords and semantic targeting without relying on user profiles.
In plain English, behavioral targeting looks at what people do—like the sites they visit or the products they browse—and tailors ads to fit their habits. Contextual targeting skips personal data and matches ads to the content of the page. So, if you're reading a blog about fitness, you'll see ads for workout gear or healthy recipes.
Let’s compare them:
| Aspect | Behavioral Targeting | Contextual Targeting |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Uses user behavior data like purchase history and online behaviors to deliver personalized experiences. | Relies on content relevance based on keywords, topics, and contextual advertising. |
| Data source | First-party behavioral data, search history, and tracking pixels. | Website content and semantic targeting through contextual analysis. |
| Privacy | Involves user profiles and may require user consent due to privacy regulations. | Privacy-friendly with no need for personal data or audience profiles. |
| Objective | Predicts purchase intent to segment users and drive conversion rates. | Targets a relevant audience using content alignment with search queries. |
| Key tools | Behavioral targeting solutions, Google Analytics, and collaboration platforms. | Contextual marketing tools and deep packet inspection for ad placements. |
Why Is Behavioral Targeting Important?
Implementing behavioral targeting can lead to a significant increase in sales growth.
That’s because its key benefits include:
Increased ad relevance: Tailoring marketing messages to individual user behavior ensures that those ads align with user interests. This results in higher engagement and, therefore, bigger sales. For instance, organizations leveraging consumer behavior data outperform competitors by 85% in sales growth.
Improved user experience: Presenting users with content that matches their preferences increases satisfaction, reduces ad fatigue, and encourages repeat interactions with your brand. Again, this leads to more sales.
Higher conversion rates: Behavioral targeting leads to more effective marketing campaigns. In fact, some studies in 2009 showed that targeted ads can double publisher revenue compared to non-targeted ads. More recently, newer studies in Europe prove that targeted ads can quadruple revenue per ad.
Efficient resource allocation: Focusing on high-value customer segments allows you to allocate your marketing budgets better. And reducing waste is a great way to increase return on investment.
What Are the Negatives of Behavioural Segmentation?
While behavioral segmentation refines targeting through user behavior analysis, the process isn't foolproof.
Here are just three negatives to consider:
Pinpointing the exact motivations behind people’s actions remains a big challenge. As a result, it can lead to misinterpretations and marketing errors.
Moreover, the costs involved in collecting and analyzing behavioral data are also significant. That means you’ll need solid analytics tools and skilled personnel to use those tools. Smaller companies may not have these resources, but even bigger companies can face implementation issues at the very least.
Ethical concerns also arise, as tracking and using personal data must balance consumer trust and respect for privacy. This topic necessitates careful handling beyond mere compliance – but we’ll discuss more about that in a second.
Now, let’s see:
Types of Behavioral Targeting
Let's dive into the various types of behavioral targeting to see how you can tailor your marketing efforts to audience actions and preferences:
1. Onsite Behavioral Targeting
Onsite behavioral targeting personalizes content for visitors based on their interactions within the same website.
Businesses can create tailored marketing messages that increase user engagement and conversion rates by analyzing user actions—such as pages viewed, time spent on specific sections, and items added to the cart.
For example, online retailers are known to track user behavior to suggest products that align with individual interests. You can typically see these messages on product pages or checkout pages, like so:
This personalization can lead to increased sales for the company and improved user experience for your prospects (because they’re getting other products to solve their pain points).
2. Network Behavioral Targeting
Network behavioral targeting tracks user behavior across multiple websites to build comprehensive profiles. That way, advertisers will use this info to deliver personalized ads based on users' browsing patterns and interests.
You’ll be using data such as visited sites, viewed content, and time spent on pages. Next, you’ll use this data to increase ad relevance and effectiveness.
Here’s an example:
Studies indicate that behaviorally targeted ads are more successful than standard run-of-network advertising. They, in fact, create greater utility for consumers from more relevant advertisements. They also have a clear appeal for advertisers who get an increased ad conversion.
3. Retargeting (Remarketing)
Retargeting, also known as remarketing, involves serving ads to people who have previously interacted with a brand but did not convert.
Like so:
This strategy keeps the brand top-of-mind, encouraging users to return and complete desired actions.
And it works.
Retargeted customers are three times more likely to click on an ad than those who haven't interacted with the brand before.
Additionally, retargeting can increase conversion rates by as much as 150%.
Basically, retargeting is extremely effective in re-engaging potential customers and boosting campaign performance.
How to Implement Behavioral Targeting Strategies [in 4 Easy Steps]
Let's explore how implementing behavioral targeting strategies can help you connect with your audience on a deeper, more personalized level:
1. Data Collection
Effective behavioral targeting hinges on precise data collection.
Tools like Google Analytics track user interactions across websites, while platforms such as Mixpanel and Hotjar offer insights into user behavior through features like heatmaps and session recordings.
Remember: Ensuring data accuracy is paramount; inaccuracies WILL lead to ineffective targeting strategies. That’s why we suggested those tools above.
But beyond those tools, you need regular data audits and validation processes to maintain data quality. After all, you want to ensure that your marketing efforts reach the intended audience with relevant content.
Pro tip: Use predictive analytics tools like Adobe Target to analyze patterns in first-party data. Combine this with frequent data hygiene checks to remove outdated user profiles. Prioritize insights from high-intent actions, such as abandoned carts or product page views, to fine-tune your behavioral targeting and increase campaign performance.
“With data collection, 'the sooner, the better' is always the best answer” - Marissa Mayer, American business executive and investor
2. Data Analysis
Effective data analysis in behavioral targeting means:
Identifying patterns in user behavior
↓ and then
Using those patterns to segment audiences accurately
You can cherry-pick advanced analytics platforms, but we like Amplitude and Mixpanel. These let businesses track user interactions and engagement metrics extremely well.
Use them to gain insights into your user behavior and then create more targeted marketing strategies. These informed decisions you make will increase user engagement and drive conversions.
Pro tip: Integrate real-time analytics from platforms into your dashboard. This allows you to immediately spot trends and anomalies in user behavior. Act on these insights by adjusting your targeting parameters to strengthen audience engagement and optimize your marketing campaigns for better results.
3. Ad Creation and Placement
Designing personalized ad content involves tailoring messages to individual user preferences, which is great for engagement.
In fact, 71% of consumers feel frustrated when a shopping experience is impersonal.
Remember: Selecting appropriate channels is equally important.
For instance, social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram offer advanced targeting options so you can reach specific demographics effectively.
TikTok also offers precise targeting but focuses more on interests and behavior, while LinkedIn zeroes in on professionals with filters like job titles and industries. Google and YouTube give you flexibility with keyword and topic targeting, plus options to reach people based on what they’re searching for or watching.
4. Monitoring and Optimization
Monitoring and optimization are integral to effective behavioral targeting.
You need to always track campaign performance through key metrics like click-through rates and conversion rates. That way, you can make timely adjustments – zeroing in on high-performance ads and replicating them.
You also need very solid A/B testing if you’re to compare different ad variations. This leads to good data-driven decisions that increase campaign effectiveness. In fact, 71% of marketers consider A/B testing their most effective optimization tactic.
Continuously analyzing performance data and iterating on strategies is how you can significantly improve user engagement and conversion rates.
Pro tip: Use heatmaps and session recordings alongside A/B testing to identify friction points in user journeys. Prioritize adjustments based on high-traffic areas and re-test after each change. Combine these insights with data from analytics platforms to refine your behavioral targeting and maximize campaign performance efficiently.
Is Behavioral Targeting Ethical?
Earlier, we noted that ethics is one of the big challenges of behavioral targeting. This tactic raises important ethical questions about privacy, consent, and the balance between personalization and consumer rights. We’ll discuss all of them right below:
Privacy Concerns and User Data Protection
Behavioral targeting and privacy concerns have become almost synonymous.
Real-time bidding (RTB) systems, for instance, can share an individual's personal data hundreds of times daily without consent, exposing users to potential misuse. These practices challenge the ethicality of behavioral targeting, as they often occur without user awareness or explicit consent. And this lack of consent undermines trust in digital interactions, basically ruining advertising for everyone.
Moreover, studies indicate that consumers knowledgeable about online behavioral targeting (OBT) are willing to pay more to keep their data private. This points to some deep-seated privacy apprehensions we all have.
Potential For Consumer Manipulation
Behavioral targeting can exploit consumer vulnerabilities by delivering personalized ads that prey on individual susceptibilities.
This isn’t just a deduction; it’s been proven.
A 2023 study highlights that online behavioral advertising can exploit decision-making vulnerabilities, creating internet infrastructure that optimizes for consumer manipulation.
For instance, algorithms may identify and target users prone to impulsive spending, promoting high-interest loans or unnecessary products. This practice raises a lot of ethical concerns about manipulation and autonomy because there’s no limit to what you can manipulate and how you can do it.
The Issue with User Autonomy
Balancing personalization with user autonomy means respecting user preferences while offering tailored experiences. The challenge is to use behavioral insights responsibly, avoiding manipulation and ensuring a fair value exchange.
Ethical behavioral targeting requires clear consent, transparent practices, and easy opt-out options.
And it brings you a slew of benefits.
Prioritizing autonomy strengthens engagement and protects your brand’s reputation in the long run. After all, when users control how their data is used, trust grows, and targeting becomes mutually beneficial.
Ad-Blocking and User Pushback
Ad-blocker usage has surged, with 42% of global Internet users employing such tools in 2024.
This trend reflects growing user resistance to intrusive advertising and privacy concerns.
To address this, we advise you to prioritize non-disruptive, relevant ads that respect user autonomy. Implement transparent data practices and offer clear opt-out options to build – or even rebuild – trust.
By aligning your advertising strategies with user preferences, you can mitigate resistance and increase engagement. This will help you create a more ethical approach to behavioral targeting.
Behavioral Targeting Examples
Now that you know the pros and challenges of behavioral targeting, let’s also look at several successful examples:
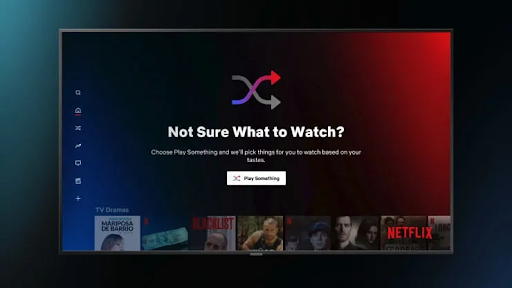
1. Netflix's Personalized Recommendations
Everyone knows that Netflix analyzes individual viewing histories to suggest content tailored to each user.
This strategy increases user engagement and satisfaction because people see relevant viewing options. This reduces the time users spend searching for content – and, more importantly, the risk of getting them frustrated in the process.
2. Amazon's Product Suggestions
Amazon uses browsing and purchase histories to recommend products that align with user interests.
We’ve all seen recommendations like these ones below:
This approach increases the quality of the shopping experience for people. And for brands, it’s great for business because it encourages repeat purchases and increases average order value.
3. Spotify's Curated Playlists
Spotify tracks user listening habits, including song preferences, skip rates, and time of day usage, to create personalized playlists like "Discover Weekly" and "Daily Mix."
This targeting increases user retention by aligning music recommendations with individual tastes, building a sense of connection and loyalty.
Behavioral Targeting in Marketing: Driving Results Ethically and Effectively
Behavioral targeting helps marketers send personalized messages based on what people do online, like their search history or shopping habits. It boosts revenue, improves conversions, and makes ads more relevant by aligning with user preferences.
But it only works if it’s done ethically—respecting privacy, being transparent, and getting consent.
Marketers also face challenges like high costs and potential pushback, all while navigating privacy laws. When done right, it balances user needs with business goals, delivering results without crossing ethical lines.
P.S. Ready to take your behavioral targeting efforts to the next level? Discover the 17 Top Meta Advertising Agencies that can help you refine your strategy and maximize campaign results. Don't miss out—click now to find your ideal partner!





























![Top 22 Paid Media Agencies to Work With in 2025 [Updated in March]](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/50baa49de4b0e51d69257e33/1705515561307-56Z45GN80B4L6J77ELDR/Top+12+Paid+Media+Agencies+to+Work+With+in+2024+%5BUpdated%5D.jpg)











